Have you ever gazed up at a clear, sunny day and marvelled at the vivid blue expanse overhead? It’s one of nature’s most enchanting phenomena, but have you ever wondered why the sky is blue? This question has intrigued people for centuries, and understanding the answer involves delving into the fascinating world of light, atmospheric science, and human perception.
The Science of Light
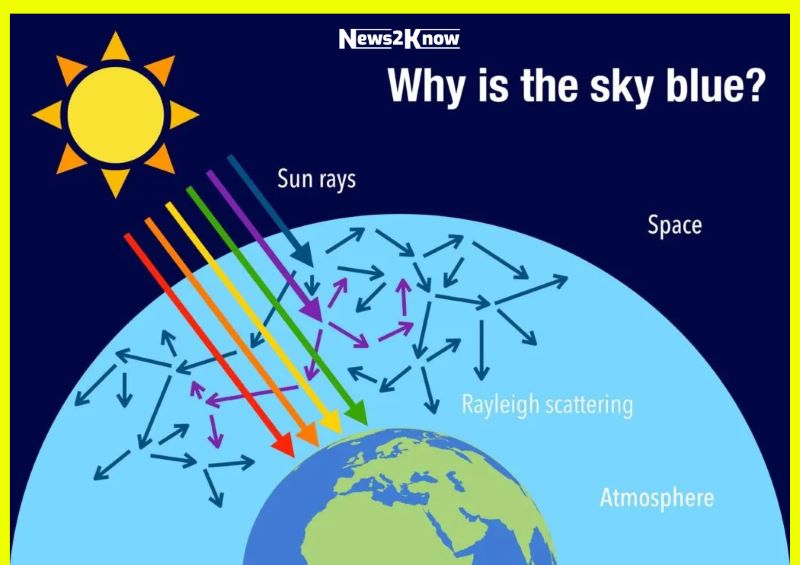
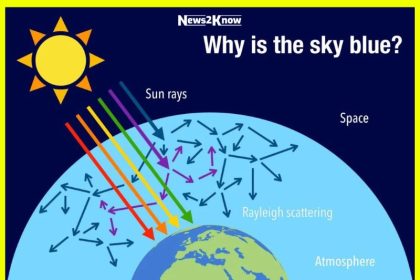
To understand why the sky is blue, we first need to explore the nature of light. Light from the sun appears white, but it’s actually a mix of different colors, each with its own wavelength. When sunlight enters Earth’s atmosphere, it interacts with the gases and particles in the air. This interaction is governed by a phenomenon called Rayleigh scattering.
Rayleigh scattering occurs because the molecules and small particles in the atmosphere are much smaller than the wavelength of visible light. When sunlight hits these tiny particles, it scatters in all directions. However, this scattering isn’t uniform across all colors. Blue light, which has a shorter wavelength, is scattered more than the other colors, which have longer wavelengths. As a result, when we look up, we see more of the scattered blue light from every direction, making the sky appear blue.
The Role of the Atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere plays a crucial role in this process. It’s made up of various gases, including nitrogen and oxygen, as well as tiny particles like dust and water droplets. These components are efficient at scattering shorter wavelengths of light, such as blue and violet. However, our eyes are more sensitive to blue light and less sensitive to violet, which is why the sky appears blue to us rather than violet.
Why Not Always Blue?
You might notice that the sky isn’t always the same shade of blue. The color can shift due to several factors:
- Time of Day: During sunrise and sunset, the sky can take on beautiful shades of orange, red, and pink. This happens because the sun is lower on the horizon, and its light has to pass through a greater thickness of the atmosphere. As a result, more of the shorter blue wavelengths are scattered out of our line of sight, leaving the longer red and orange wavelengths to dominate.
- Weather Conditions: Clouds, pollution, and other atmospheric particles can affect the color of the sky. For example, a hazy sky might look pale blue or even grayish due to increased scattering of light by larger particles or pollutants.
- Altitude: At higher altitudes, where the atmosphere is thinner, the sky can appear darker blue. This is because there are fewer molecules and particles to scatter the light, allowing the blue color to be more intense.
Why Does This Matter?
Understanding why the sky is blue isn’t just about satisfying curiosity. It connects to broader principles in science, such as optics and atmospheric chemistry, and it helps us appreciate the delicate balance of natural processes that create our environment. It also underscores the importance of maintaining air quality, as pollutants can alter the scattering of light and impact our view of the sky.
Blue Sky In Summary
The blue sky is a beautiful example of how simple physical processes can create such a stunning and familiar part of our daily lives. The phenomenon of Rayleigh scattering ensures that our skies are predominantly blue during the day, creating a backdrop for everything we do. So next time you look up and admire the blue sky, you’ll know that it’s not just a visual treat—it’s a testament to the wonderful complexities of nature at work.
Keep exploring, and the world around you will continue to reveal its hidden wonders. The sky is blue not just because of the science behind it, but because of the way it connects us to the vast, intricate tapestry of our planet’s atmosphere.